I have a lot of fun doing this project. Not only do I know the entry-level of doing data processing but also find those powerful tools.
What conditions need distributed batch processing
- Static data
- Independent to each other
- Not real time
- unstructured data otherwise just data warehousing
Batch Processing with MapReduce
Two tasks:
- N-gram
- Probabilistic Language Model
Figure explains the procedure:
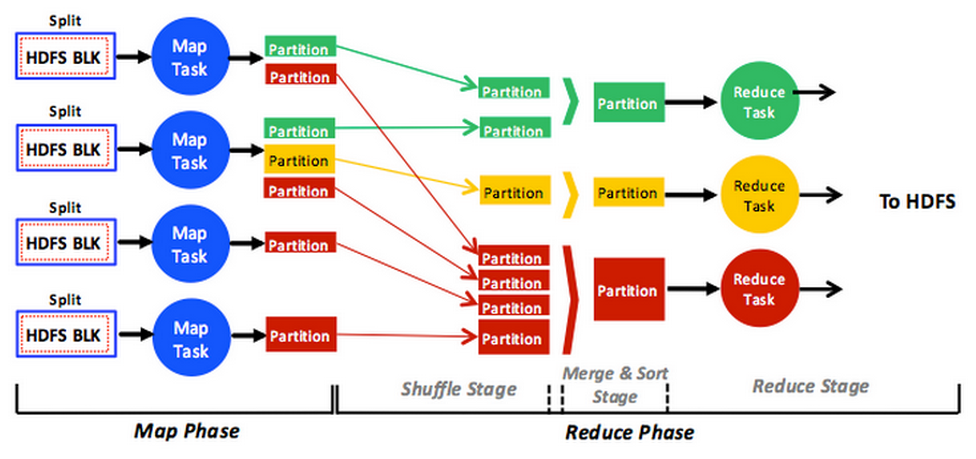
Treats to save speed and space: use combiner which is identical to reducer but right after mapper. Therefore, it is like preprocessing.
Some background knowledge for fault-tolerant:
- Data replication: underlying HDFS handle this
- Task failure or slowdown
- Node failures: slave node dies, lost heartbeat to master node. Primary node dies, use secondary master node (i think it is only available in yarn (hadoop 2.0))
This task was to Ngram Count Model:
- 8 GB wikipedia 1 day dataset in XML format
- I should not use hadoop stream but write our own batch processing program
- Only need 5 grams, 1 gram : ‘this’ count 1, 2 gram : “this is” count 1 …
Some special handling for the input data, I did it in the Mapper Class mainly:
- Use utf-8 as encoding
- Escape character like this... blahblah, i use `org.apache.commons.lang.StringEscapeUtils` to help me with the task
- Removed html links
The idea of writing batch processing program for Mapper and Reducer:
- A static class to extends Mapper class <”Input Key Format, Input Value Format, Output Key Format, Output Key Value Format”>
- Override map() method
- A static class to extends Reducer class <”Input Key Format, Input Value Format, Output Key Format, Output Key Value Format”>
Instance used on AWS:
- 6 large instances
Probabilistic Model:
Actually it is based on conditional probability.
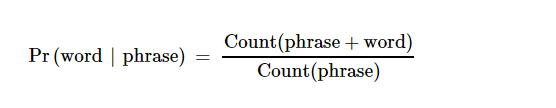
Tools used:
- Hbase 1.3.0
- Hadoop 2.7.3
- AWS EMR (5.4.0)
Recommended schema for Hbase:
- Phrase as row key
- Words that possibly appear as columns and store the possibility in the cell
Some notes:
- It was recommended use
TableMapReduceUtilclass to direct the output of Reducer class to HBase - I had hard time to connect to Hbase
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create(); conf.set("hbase.master", "your master node:16000"); conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "your zookeeper node normally same as master node"); conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientport", "2181"); // After we set up the configuration, get a job instance Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "probability table"); job.setJarByClass(ProbabilityTable.class); //I read from HDFS (mapper) (Use the defualt identity mapper class direct to output) job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class); // And then we can use table map reduce utilization job TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob( "words", // output table TablePredictReducer.class, // reducer class job); job.setReducerClass(TablePredictReducer.class); // Configure Map output part job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); - I use heap sort to get the most possible answers
Another exciting part of the project is I can use the expensive Redis. I directly write the whole database into Redis (key value data structural store).
Amazon ElasticCache is used for Redis.
I have to design my output format class for Redis after the reducer part. The difficulty also comes from here.
- Write a class to extent
FileOutputFormat, this is similar to HBase, I did not modify the key value type for the Reducer class but define my own FileOutputFormat then, hadoop will not output to hdfs but directly to Redis - Override the getRecordWriter
- Also requires a protected to extend RecordWriter